| |
|
|
|
| |
Common Defects in Web Applications |
|
|
|
| |
Quality of product/ service is the area where no customer is prepared for a
compromise. Effective and efficient test execution, thus, holds the key to earn and
maintain customer good will for continued association and manage customer loyalty.
Defect Prone Zones are the areas in the web applications that are prone to the
common defects. Security, Miscellaneous data and Unconventional usage of keys etc.
are the types of Defect Prone Zones. The functionalities like Security, Miscellaneous
data and Unconventional usage of keys should be supported by all the applications
irrespective of the domain, criticality and user levels. This may not be listed in the
Business Requirements, Use Cases or User Interface Design Documents, but it should
be ensured that the web applications are supporting these functionalities. But
considering the project pressure, it is difficult to incorporate all the business
requirements within the given schedule. Hence incorporating these additional
functionalities in the given time is next to impossible. It is the responsibility of the testers
to validate these functionalities and ensure that these are available in all the web
applications (common defects are not present).
The basics of the Test Maturity Model states that, there is always a scope for
improvement. Being an ISO 9001: 2000 certified and SEI CMM Level 5 company,
Cognizant Technology Solutions has experimented proactively in evaluating the ways for
maturity / improvement. One of the key initiatives taken for improving the test efficiency
is the identification of the common defects and testing the same in all the web
applications. This has caused a considerable reduction in defect leakage and in turn
customer satisfaction.
This paper details the common defects that are present in web applications and
also mention the improvement in the test efficiency, with minimum increase in effort. |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Introduction |
|
|
|
| |
Testing as performed in most of the organizations is a process designed to
compensate for an ineffective software development process. It is risky to develop
software and not test it. As long as developmental and maintenance processes that
organization utilize continue to introduce defects into software, testing will be very
important component of the developmental process.
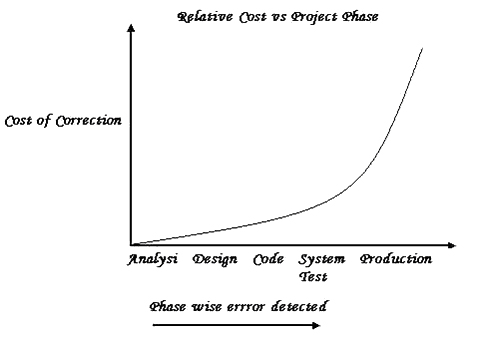
Testing Cost depend heavily on when in the project life cycle testing occurs. The
later in the life cycle testing occurs, the higher the cost. As defects would be identified in
the later stage of testing cycle and the cost of a defect is twofold; you pay to identify and
to correct it. The cost of defect identification and correction increases exponentially as the project phase progresses. Figure illustrates the cost incurred for eliminating a defect. |
|
| |
 |
|
|
| |
Apart from eliminating defects which are variance from specification, there are
certain defects which we overlook at times, this might not be listed in Business Rules/
Use Case / UIDD, still it should be ensured that our applications are supporting these
features. But considering the project pressure, the developers are finding it difficult to
incorporate all the common standards/ Procedures within the given schedule. Hence
they may not be able to incorporate these additional features in the given time. So, we
testers should take the initiative of validating them and ensuring the availability of these
features (absence of common defects). This document details these common defects
that are present in web applications. With the advent of common defect, test efficiency
can be improved with minimal effort.
To read the complete article please click here.
|
|
|
|



